Introduction to Helium
Imagine a wireless network that is not controlled by a single entity, where anyone can participate and contribute to the network’s growth. This is precisely what Helium offers. Through a unique combination of blockchain technology, a native token, and an ingenious consensus protocol, the Helium Network has created an ecosystem that rewards those who provide wireless network coverage and enables devices to connect to the internet in a decentralized and secure manner.
The Helium Network functions on a custom-designed blockchain, harnessing the rapid, expandable, and secure structure of the Solana Blockchain. This strategic foundation has ushered in a realm of fresh possibilities for innovation, enabling the connection of IoT devices through the LoRaWAN network and delivering swift mobile connectivity via the 5G network.
In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of the Helium Network, its native token HNT, and its expansion onto the Solana Blockchain. We’ll explore its distinct characteristics and operations, as well as the security protocols implemented to safeguard both the network and its participants.
Overview of Helium Network
The Helium Network represents a fresh and inventive approach to linking devices to the internet. It operates in a decentralized fashion, free from the control of a single company or organization. Instead, it relies on a network of Hotspot Owners, Miners, and Routers.
Hotspot Owners, who can be individuals or organizations, play a pivotal role by setting up and maintaining Hotspots. These Hotspots act as nodes in the network, providing wireless coverage to specific geographic areas. Miners, on the other hand, serve as the verifiers of wireless network coverage. They operate Hotspots and are required to submit cryptographic proofs, confirming their coverage in designated locations.
IoT Devices, equipped with the necessary hardware and firmware compatible with the Helium Network’s protocol (WHIP), connect to nearby Hotspots. These devices encompass a wide array of IoT applications, from environmental sensors to smart meters. Routers function as intermediaries, facilitating the seamless transfer of data between Devices and the internet. They specify the price they are willing to pay for the data transmitted by Devices.
At the core of the Helium Network lies its unique consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-Coverage (PoC). This innovative algorithm requires Miners to provide cryptographic proofs of their wireless network coverage, effectively verifying the honesty of their coverage claims.
The network operates on a custom-built blockchain infrastructure, powered by its native token, HNT. HNT is instrumental in incentivizing network participants and enabling secure transactions. Data transmission occurs through low-power, wide-area network (LoRaWAN) technology, utilizing the WHIP protocol.
Data Credits are an essential component of the network, ensuring transaction reliability and security. These credits are a form of payment for data transfer and are pegged to USD, mitigating the typical volatility associated with cryptocurrencies. Miners are rewarded with freshly minted HNT tokens for their contributions; including network coverage, data delivery, and participation in blockchain block creation. A Miner’s chances of being elected to the consensus group are influenced by the quality of their wireless network coverage, as validated through PoC.
The Helium Network also places significant emphasis on security. It minimizes potential attack vectors by not requiring open inbound ports for Hotspots. Furthermore, LoRaWAN devices used in the network feature built-in AES private key encryption at the chip level.

Team and Background
The Helium Network’s team comprises talented individuals from diverse backgrounds, including technology, blockchain, networking, and IoT. Their collective expertise and dedication have driven the network’s growth and innovation. The team’s members include software developers, blockchain experts, IoT specialists, and business leaders who are committed to realizing the network’s mission.
Here’s a closer look at the founders and key team members behind Helium:
Amir Haleem: As one of the co-founders of the Helium Network, Amir Haleem brings a wealth of experience in technology and entrepreneurship. His vision has played a pivotal role in shaping the network, with a focus on establishing a decentralized wireless infrastructure to support the Internet of Things (IoT).
Shawn Fanning: Shawn Fanning, a co-founder of the Helium Network, is renowned for his pioneering work as the creator of Napster, the pioneering peer-to-peer file-sharing platform. His experience in creating innovative, disruptive technologies has contributed significantly to Helium’s ethos of innovation and decentralization.
Sean Carey: As another co-founder of Helium, Sean Carey’s expertise in technology and his passion for creating a people-powered wireless network have been instrumental in shaping the network’s vision.
BACKGROUND
The Helium Network was founded in 2013 with a vision to create a decentralized wireless infrastructure that could support the rapidly growing Internet of Things (IoT) industry. The founders aimed to lower the barriers to entry for IoT connectivity and to create a people-powered network driven by economic incentives.
In 2019, Helium introduced its primary offering, the Helium Hotspot. This device enabled users to extend wireless connectivity to IoT devices using a novel protocol known as LongFi. LongFi combines the extensive coverage of LoRaWAN with the Helium blockchain. Early enthusiasts began deploying Hotspots to earn HNT tokens as compensation for offering network coverage.
With an increasing number of Hotspots being deployed worldwide, the Helium Network experienced ongoing expansion, drawing the attention of developers, businesses, and individual users. This growth extended the network’s reach to diverse countries, opening doors to fresh applications and reinforcing its role as a provider of decentralized wireless infrastructure.
In September 2022, the Helium community approved HIP 70. It essentially involved shifting Proof-of-Coverage and Data Transfer Accounting to Oracles and transferring transactions and accounts to the high-performance Solana blockchain. The decision was backed by a record number of individual wallet votes, with over 12 million HNT in favor of the change. The move was a significant step for Helium, moving from a concept to a scalable reality.

Helium’s Migration to Solana
To ensure continued growth, the Helium community recognized the need for a new architecture for its L1 blockchain last year. The decision came about because the core developers were dedicating a significant amount of time to maintain the Helium blockchain, mainly due to the increasing difficulty in handling two crucial aspects of the network: proof of coverage and dependable data transfer.
In response to these challenges, the Helium community reached a consensus and successfully passed a proposal to enhance the network by transitioning to the Solana blockchain. The move was aimed at addressing these issues and positioning Helium for sustained success in the long run.
The migration of the Helium Network to the Solana blockchain was a pivotal milestone in the network’s evolution. This transition, completed in April 2023, has brought about several significant enhancements and advantages for the Helium ecosystem:
Scalability and Performance: The transition to Solana brings significant advantages, with scalability being a primary one. Solana is well-known for its capacity to manage thousands of transactions per second, positioning it as an excellent fit for the fast-growing Helium Network. Solana’s remarkable throughput capabilities guarantee that the Helium Network can efficiently handle the substantial volume of transactions stemming from IoT devices and other network participants.
Speed: Solana offers rapid transaction processing, with transactions executed in mere seconds. This increased speed is a crucial feature for the Helium Network, as it allows for real-time connectivity for IoT devices and other applications. This faster transaction processing contributes to a more seamless and user-friendly experience for network users.
Security: Security is paramount for the Helium Network, particularly because it powers a diverse range of IoT devices. Solana’s robust security features align well with the network’s requirements, ensuring the safe and secure operation of the ecosystem.
Interoperability: Solana is compatible with many other blockchains, enabling the Helium Network to seamlessly integrate with other projects and applications within the Solana ecosystem. This interoperability expands the network’s capabilities and opens up new opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
Cost Reduction: Transaction fees will significantly drop, with an average fee of $0.00025 on Solana compared to the previous $0.35 on Helium’s blockchain.
DeFi Access: The move to Solana provides access to a rich and diverse DeFi ecosystem, offering opportunities for HNT, IOT, and MOBILE token owners to participate and earn rewards through platforms like Orca and Kamino. The Helium Wallet app will also directly connect to DeFi.
Open Source Development: The migration to Solana opens up opportunities for developers to build on top of Helium’s core technology, making it a foundational layer for projects requiring wireless connectivity.
The Helium Network’s migration to Solana has achieved remarkable success, witnessing the transfer of more than 100 million HNT tokens since its inception. This bridge has not only streamlined token transfers but has also catalyzed the creation of fresh Helium-driven applications. Among them is Helium Pay, which empowers users to utilize HNT tokens for purchasing goods and services, thereby, enhancing the practicality and reach of the native token.
The migration has enabled the network to support the rapid growth of IoT devices and applications while maintaining its commitment to decentralization and innovation. The bridge to Solana has not only strengthened the network’s technical capabilities but has also expanded its potential for real-world applications and use cases.
Helium Network Tokens
The Helium Network incorporates a variety of tokens, each serving specific purposes and catering to different aspects of the network’s functionality. Here’s an overview of the different tokens within the Helium Network:
HNT (Helium Network Token): HNT is the native cryptocurrency and protocol token of the Helium Network. It plays a central role in incentivizing and facilitating network participants and transactions. HNT serves the needs of two primary parties within the Helium ecosystem:
Hotspot Hosts and Operators: Hotspot Hosts receive network tokens like IOT or MOBILE when they deploy and maintain network coverage. These network tokens can be redeemed for HNT.
Enterprises and Developers: HNT serves as a means for enterprises and developers to establish connections for devices and create IoT applications. For covering transaction costs related to wireless data transfers on the network, Data Credits are employed. These credits are directly linked to the USD and are obtained from HNT through a burn transaction.
IOT Token (IoT Network): The IOT token is the protocol token specific to the Helium IoT Network. It was introduced through community proposals and is used in the LoRaWAN subnetwork. IOT tokens are minted through data transfer proceeds and Proof of Coverage mechanisms. Like other protocol tokens, IOT is always backed by HNT and can be converted into HNT based on a redemption ratio calculated algorithmically.
MOBILE Token (5G Network): The MOBILE token serves as the protocol token for the Helium Mobile Network. It facilitates high-speed mobile connectivity and data transmission within the 5G subnetwork. MOBILE tokens, like other protocol tokens, are backed by HNT and can be converted to HNT based on a redemption ratio determined by the network’s utility score.
Data Credits: Data Credits are a fundamental mechanism on the Helium Network, ensuring that all usage is paid for and accounted for. These credits can be used interchangeably on any network within Helium, but once created, they cannot be redelegated. Data Credits serve as the payment method for data transfers on the Helium IoT and Mobile networks. Notably, they are designed to be stable, as one Data Credit is equivalent to $0.00001 USD.
These tokens collectively provide a comprehensive framework for incentivizing network participation, enabling data transmission, and maintaining the economic integrity of the Helium Network. They also ensure that network participants are rewarded for their contributions, whether they are Hotspot Hosts providing coverage, Miners validating coverage, or developers creating IoT applications. The Helium Network’s token ecosystem supports the network’s growth and expansion while offering versatility for various network use cases.
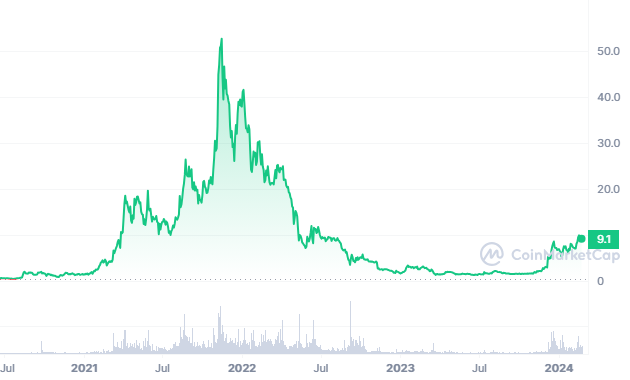
$HNT Market Stats:
Market Cap: $395,135,773
Circulating Supply: 137,502,425HNT
Supply Cap: 223,000,000
All-Time High: $54.88
All-Time Low: $0.113248
Initially, the HNT token had a good start, with its trading value hovering around $0.50 before gradually rising to $2.00 within a span of two months. However, its price experienced a dip the following month, settling at $1.25, but it managed to regain its momentum and was back at $2.00 by October 2020. Although it briefly fell below $1, it soon bounced back, and by the start of 2021, it was trading at approximately $1.25.
HNT can be purchased on various cryptocurrency exchanges such as Binance, Bybit, FTX, Crypto.com Exchange, and KuCoin.
Core Features and Functionalities of Helium
The Helium Network offers a set of features and functionalities that distinguish it as a decentralized, secure, and scalable wireless infrastructure. Here are the key features and functionalities of the Helium Network:
Proof-of-Coverage (PoC): The Helium Network utilizes a unique consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Coverage. Miners, who operate Hotspots, provide cryptographic proofs to verify their wireless network coverage in specific geographic locations. PoC ensures that Miners are honestly representing the coverage they provide, enhancing the quality and security of the network.
Blockchain and HNT: The network operates on its custom-built blockchain infrastructure, powered by the native cryptocurrency and protocol token, HNT. HNT plays a central role in incentivizing and facilitating network participants, including Hotspot Owners, Miners, and developers.
WHIP Protocol: The Helium Wireless Protocol (WHIP) is an open-source and standards-compliant wireless network protocol designed for low-power Devices operating over vast areas. WHIP facilitates secure and efficient data transfer between Devices and the internet, offering a seamless and reliable communication channel.
Proof-of-Location: Proof-of-Location is a system for determining a Device’s physical geolocation using WHIP, eliminating the need for expensive and power-hungry satellite location hardware. Devices can securely and immutably declare their location at a specific moment, which is recorded on the blockchain.
Helium Consensus Protocol: This is an innovative consensus protocol that creates a permissionless, high-throughput, and censorship-resistant system. This is achieved by combining an asynchronous Byzantine fault-tolerant protocol with identity verification through Proof-of-Coverage.
DWN: It introduces a wireless network that offers internet access to Devices through numerous independent Miners. The Helium network and WHIP specifications, to which participants in the Helium network must adhere, are also outlined. Routers compensate this network of Miners for facilitating data transfer to and from the internet, while Miners receive newly minted tokens as rewards for providing network coverage and transmitting Device data to the internet.
Data Credits: Data Credits are an integral part of the network, serving as the payment method for data transfers. These credits are pegged to the USD, providing stability in a typically volatile cryptocurrency environment. Data Credits are used to pay transaction fees for wireless data transmissions on the network.
Scalable and Secure: The Helium Network leverages the Solana Blockchain, known for its high scalability, low latency, and robust security. This ensures the network’s ability to handle a large number of transactions generated by IoT devices and other participants.
Versatile Use-Case Coverage: The Helium Network is adaptable, accommodating a diverse array of use cases. It caters to IoT devices through the LoRaWAN network and offers swift mobile connectivity via the 5G subnetwork. This flexibility opens the door to the development of a multitude of IoT applications.
Incentivized Participation: Network participants, including Hotspot Owners and Miners, are rewarded with tokens for their contributions. Hotspot Hosts, in particular, receive network tokens that can be redeemed for HNT, creating economic incentives for network expansion and maintenance.
These core features and functionalities collectively create a robust ecosystem that fosters decentralization, security, and innovation in the realm of wireless connectivity.
Security of Helium network
Security is a paramount concern within the Helium Network, which is built on the principles of decentralization and cryptographic security to ensure the integrity and reliability of its operations. Helium employs a number of security measures and practices that safeguard the Network.
In the interest of bolstering network security, the Helium Hotspot no longer demands open or forwarded inbound ports, which is one of the most common attack vectors for network devices. This change significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to network devices.
For IoT devices operating within the Helium Network, especially those in the LoRaWAN subnetwork, a strong layer of security is established through hardware-level features. These devices incorporate AES private key encryption at the chip level, assuring the privacy and security of transmitted data.
To facilitate secure and stable network transactions, Data Credits are introduced as a payment mechanism on the Helium Network. These credits are pegged to the USD, eliminating the volatility typical of cryptocurrency-based networks. This enhancement creates a more predictable and secure environment for users.
Helium wallets, including those integrated into the Helium App, employ asymmetric keys to safeguard private keys. This robust encryption ensures the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive key information.
The network’s consensus mechanism, PoC, plays a vital role in upholding the integrity of network coverage. Miners are mandated to produce cryptographic proofs of their wireless network coverage, validating the accuracy of their claims. This mechanism guarantees that Miners consistently provide honest and reliable network coverage.
By integrating these security measures and best practices, the Helium Network strives to create a secure and resilient wireless infrastructure. The network’s commitment to safety and the ongoing enhancement of security features reinforces its position as a trusted and innovative platform for IoT and wireless connectivity.
Risks challenges and how Helium tackles them
Challenges Faced by the Helium Network:
Network Growth and Scalability: The rapid expansion of the Helium Network poses challenges in terms of scalability. As more Hotspots are added and more IoT devices join the network, ensuring that it can handle the increased transaction volume becomes crucial.
Security Concerns: The network must remain vigilant against potential security threats. Any vulnerability in the network could be exploited, leading to issues such as unauthorized data access or tampering with Proof-of-Coverage (PoC) mechanisms.
Economic Viability: Sustaining the economic incentives for Hotspot Hosts and Miners is essential for network growth. Ensuring that the rewards are attractive and proportional to their contributions is an ongoing challenge.
Steps Taken to Mitigate Challenges:
Migration to Solana: The migration to the Solana Blockchain enhances the network’s scalability, security, and interoperability. Solana’s high transaction throughput and low latency bolster the network’s capacity to handle growth and collaborate with other blockchain projects, mitigating potential interoperability challenges. This move also strengthens the network’s security and resilience.
Security Safeguards: Ongoing security examinations and evaluations are carried out to pinpoint and rectify potential weaknesses. The Helium Network maintains a watchful stance and stays agile in the face of developing security risks, all in the interest of preserving the network’s safety and soundness.
Regulatory Compliance: The Helium Network actively collaborates with legal and regulatory experts to navigate the complex landscape of regional regulations. Ensuring compliance and transparency is a priority as the network grows.
Economic Incentives: To maintain the economic viability of the network, the allocation of HNT tokens is carefully managed based on factors like network utility score. This ensures that rewards for Hotspot Hosts and Miners remain attractive and proportional to their contributions, incentivizing network growth.

Conclusion
The Helium Network operates as a decentralized wireless network that harnesses the power of blockchain technology to deliver dependable and secure wireless connectivity for IoT devices. This represents a distinctive and pioneering method for wireless networking that champions decentralization, security, and inclusiveness.
The Helium Network is still under development, but it has already made significant progress. The network has over 200,000 Hotspots deployed worldwide, providing coverage to over 20 million square miles. Helium is also partnering with a growing number of companies to develop and deploy IoT devices on the network.
The Helium Network has the potential to revolutionize the way we connect devices to the internet. It is a decentralized and secure network that can provide affordable and reliable connectivity to IoT devices in even the most remote locations. The Helium Network is also interoperable with other blockchain networks, making it a valuable addition to the emerging Web3 ecosystem.




