Introduction
Kujira Network emerges as a groundbreaking Layer 1 blockchain ecosystem, meticulously crafted upon the robust Cosmos SDK and secured by the Tendermint consensus mechanism. It aspires to revolutionize the decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape by offering a comprehensive suite of sustainable financial tools and technologies tailored to the multifaceted needs of web3 enthusiasts.
Overview
Kujira boasts a state-of-the-art native bridge renowned for its secure, efficient, and interoperable infrastructure. This robust bridge harnesses the power of Axelar’s cross-chain communication technology, seamlessly facilitating asset transfers and cross-chain transactions between a multitude of supported networks, including Kujira, Cosmos, Ethereum, Arbitrum, and beyond.
Delving into the technical intricacies, the Axelar Bridge embedded within the Kujira ecosystem stands as a decentralized network specifically designed to orchestrate cross-chain communication and asset transfers between disparate blockchain networks. This sophisticated mechanism leverages a combination of Gateway smart contracts, validators, and relayer servers to seamlessly execute these transactions.
Kujira meticulously curates protocols and tools designed for builders and users seeking transformative FinTech solutions within the blockchain realm.
Kujira blockchain, architected with a hybrid approach, defies categorization as a purely modular or monolithic blockchain. Instead, it deftly harnesses Cosmos’ modular software suite of software development kits (SDKs) as its fundamental framework while simultaneously integrating natively developed DApps. This intricate blend fosters a robust ecosystem capable of hosting a diverse range of decentralized applications.
Background
Kujira is a decentralized ecosystem that aims to provide sustainable and innovative solutions for the Web3 space. Kujira leverages the power of cross-chain interoperability, liquidity mining, and algorithmic trading to create a platform that supports various protocols, builders, and users. Kujira has its own native token, KUJI, that is used for governance, staking, and rewards.
Kujira is built on the Arbitrum network, which is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that offers fast and cheap transactions. Arbitrum uses a technique called optimistic rollup, which allows users to execute transactions on a sidechain and periodically post proofs to the main chain. Arbitrum claims to offer near-instant finality, low fees, and high throughput, while maintaining the security and decentralization of Ethereum.
Kujira has launched its first product, Camelot, which is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that allows users to swap, provide liquidity, and earn tokens on Arbitrum. Camelot also features a unique mechanism called Nitro Boost, which rewards users for providing liquidity to low-volume pools. Kujira plans to launch more products in the future, such as Grail, which is a decentralized protocol that enables users to create and execute algorithmic trading strategies on Arbitrum.
Kujira is one of the most promising projects in the Arbitrum ecosystem, as it aims to bridge the gap between traditional and decentralized finance. Kujira has a strong team of experts from Google, IBM, and Stanford, as well as a supportive community of users and investors. Kujira is also backed by reputable partners and investors, such as Axelar, Solana, and Polygon. Kujira is on a mission to create a Web3 API economy, where data providers and consumers can benefit from the power of decentralized and scalable data feeds.
Launch of Kujira Mainnet
Kujira’s independent Layer 1 blockchain journey took a monumental step forward with the successful launch of its mainnet, establishing a robust foundation for decentralized applications and financial services.
Introduction of ORCA
Pioneering the Kujira Network’s ecosystem, ORCA emerged as the first application, introducing a transparent and fair bidding mechanism for liquidated collateral.
Governance Vote for Token Burn
Through a community-driven governance vote, a portion of $KUJI tokens were designated for burning, strategically adjusting the tokenomics to align with the network’s long-term objectives.
Educational Initiatives
Championing blockchain education, Kujira established Kujira Academy, empowering users to navigate the intricacies of decentralized finance (DeFi) and confidently engage with the network
Axelar Bridge Integration
Kujira embraced cross-chain interoperability by integrating Axelar’s technology, enabling seamless and secure asset transfers between supported blockchains.
Tokenomics
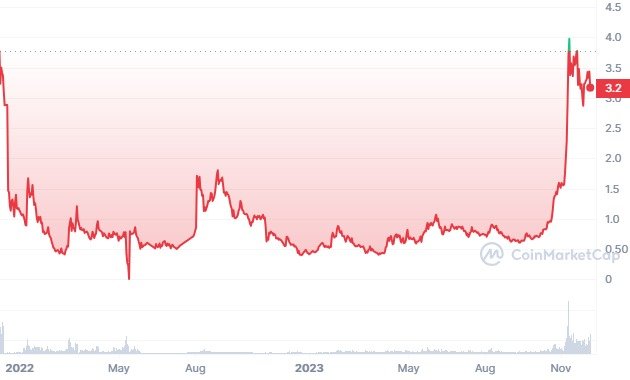
The Kujira Network revolves around its native token, $KUJI, which serves as the cornerstone of its intricate tokenomics model. Let’s delve into some key aspects of $KUJI’s tokenomics:
The total supply of $KUJI tokens is fixed at 122,398,190.844391 (approximately 122.4 million tokens), representing the maximum number of tokens in circulation. This supply was initially set at 150 million tokens but was subsequently reduced following a governance vote on January 18, 2022, with liquidity pool rewards being burned to achieve this revised supply.
The $KUJI token plays a multifaceted role within the Kujira Network, encompassing both governance and financial utilities. It serves as the primary medium for paying network fees and transaction costs associated with dApps hosted on the Kujira blockchain. These collected fees are not simply stored but rather distributed to $KUJI stakers, incentivizing network participation and promoting the security and stability of the Kujira ecosystem.
The $KUJI token’s initial release occurred through a token generation event in November 2021. This launch followed a carefully structured schedule that incorporated vesting periods for different token allocations, ensuring a balanced and controlled distribution. The token distribution plan encompassed varying vesting periods for different allocations, such as:
– Private Sale: 27.975 million tokens, subject to a 12-month vesting period.
– Public Sale: 21 million tokens, distributed with a 6-month vesting period.
– Liquidity Provision: 6 million tokens allocated for liquidity provisioning initiatives.
– Advisors: 7.5 million tokens allocated to advisors and contributors, subject to a 12-month vesting period.
– Team: 27 million tokens allocated to the core team, subject to a 24-month vesting period.
– Operational Fund: 11.025 million tokens reserved for ongoing operational expenses and long-term ecosystem development initiatives, subject to a 24-month vesting period.
– Marketing: 6 million tokens allocated for marketing and community engagement initiatives, subject to a 24-month vesting period.
– Airdrops: 500,000 tokens distributed through community airdrop initiatives (number adjusted after the burn).
– Treasury Reserve: 6.75 million tokens earmarked for strategic ecosystem development initiatives and long-term ecosystem sustainability, subject to a 24-month vesting period.
– Community Rewards: 8.648 million tokens allocated for incentivizing ecosystem participation and rewarding community contributions (number adjusted after the burn).
The current token distribution schedule is anticipated to be completed by November 9, 2023, at 12 pm UTC, marking the point at which all tokens will have been fully released from their respective vesting periods.
The sustainability of the $KUJI token stems from its non-inflationary nature and its reliance on the proliferation and adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) built on the Kujira ecosystem to generate fees. This self-sustaining model ensures that stakers are rewarded through a portion of the fees paid on Kujira dApps, such as FIN, directly aligning token value with the growth and utilization of the Kujira ecosystem.

Features and Functionality
- Sustainable Sovereign Layer 1 Ecosystem: Kujira, a sovereign Layer 1 blockchain, champions sustainable FinTech solutions that empower protocols, builders, and web3 users to innovate and thrive within the decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape.
- Hybrid Blockchain Architecture: Powered by the Cosmos SDK, Kujira strikes a balance between modularity and monolithicity. While leveraging Cosmos’s comprehensive suite of software development kits (SDKs) for its underlying architecture, Kujira seamlessly integrates natively built dApps, fostering a unified and dynamic ecosystem.
- Semi-Permissioned Model: Kujira embraces a semi-permissioned model, ensuring a high level of quality and reliability within its ecosystem. New dApps undergo a rigorous approval process by the protocol’s governance body, safeguarding the network’s integrity and fostering a trusted environment for users.
- Cohesive DeFi Structures: Adhering to a philosophy of cohesive DeFi structures, Kujira cultivates a harmonious ecosystem where dApps interact synergistically, maximizing the collective potential of the network.
- User-Friendly Programming Language: Kujira employs Rust, a user-friendly programming language with an expressive type system, enhancing the development experience and attracting a broader pool of developers to contribute to the ecosystem.
- Streamlined Development Framework: Leveraging the CosmWasm framework, Kujira streamlines the application development process. Developers benefit from predefined templates, build systems, and contract tests, enabling them to efficiently create and deploy secure smart contracts.
- Focus on Real Yield: Kujira prioritizes solutions that deliver real yield, emphasizing cost-effectiveness, user-friendly UI/UX, and interoperability. By democratizing access to investment opportunities, Kujira empowers retail investors to participate in the DeFi space alongside institutional players, regardless of market conditions.
- Revenue-Generating Products: Kujira pioneers a range of innovative and revenue-generating products, transforming payment infrastructure and unlocking new possibilities for the DeFi ecosystem.
Advantages of Kujira Network
- Pioneering Sustainable FinTech: Kujira emerges as a beacon of stability amidst the dynamic web3 landscape, unwavering in its commitment to providing sustainable financial technology solutions that foster long-term growth and prosperity.
- Quality and Reliability: Kujira enforces a semi-permissioned model, ensuring that all dApps undergo a rigorous approval process by the protocol’s governance body. This vetting process safeguards the network’s integrity and instills trust among users.
- User-Friendly Development: The utilization of the Rust programming language and the CosmWasm framework empowers developers to craft smart contracts effortlessly. This synergistic combination fosters a streamlined and user-friendly development process, inviting a broader spectrum of developers to contribute to the ecosystem.
- Efficiency and Lower Fees: By employing an on-chain scheduler, Kujira effectively diminishes the dependency on bots, minimizing the instances of wasted transactions and redirecting the fees that would otherwise incentivize bot usage back to the hands of the network’s users. This innovative approach promotes a more equitable and efficient transaction fee structure.
- Speed for Intensive Strategies: By shortening block time, Kujira can alleviate congestion and provide a better user experience, which is essential for strategies like high-frequency trading.
Risks and Challenges
- Market Volatility: Much like any blockchain network, Kujira navigates the dynamic realm of cryptocurrency markets, where fluctuations in token prices can influence the stability and adoption of its native tokens and services.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The ever-changing regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies and DeFi platforms poses a challenge for Kujira, as potential regulatory changes could impact its operations and user base.
- Security Risks: Despite rigorous efforts to uphold stringent code standards, the network remains susceptible to security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors, potentially leading to loss of funds or disruptions to network operations.
- Competition: Navigating the highly competitive landscape of established and emerging blockchains poses a challenge for Kujira, as increased competition could impact its market share and overall growth trajectory.
- Adoption Hurdles: Acquiring a substantial user base and fostering widespread adoption of its DApps and services poses a significant challenge, particularly in light of the complexity of blockchain technology for the average user.
- Technical Complexity: Balancing the technical complexities of maintaining and upgrading a blockchain network, coupled with the ongoing pursuit of interoperability with other chains, demands dedication and a commitment to sustainable resource allocation, ensuring Kujira’s resilience and long-term growth.
- Dependence on Cosmos SDK: As a blockchain built upon the Cosmos SDK’s modular architecture, Kujira’s performance could be indirectly affected by potential issues or limitations within the broader Cosmos ecosystem.
How the Kujira Network Addresses these Challenges
- Innovative DApps: To address specific DeFi challenges and provide user-friendly functionality, Kujira has developed a suite of four DApps: FIN, ORCA, BLUE, and Finder.
- Community Governance: To foster decentralization and ensure that the community’s values are represented, Kujira has established the Kujira Senate, a governance structure that empowers knowledgeable and trusted community members to influence the network’s decisions, regardless of their $KUJI holdings.
- Security Measures: Kujira’s semi-permissioned model and stringent standards for DApps indicate a proactive approach to maintaining high-quality code and mitigating the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Market Positioning: By prioritizing affordability and user-friendliness in its DeFi investment tools, Kujira strives to democratize access to decentralized finance, empowering every individual to become a crypto whale. This inclusive approach positions the network for broader adoption and expansion, potentially revolutionizing the DeFi landscape.
- Ecosystem Growth: Harnessing the power of the Cosmos SDK, Kujira seamlessly integrates with other blockchains, fostering cross-chain interoperability and expanding its reach within the dynamic DeFi landscape. This strategic approach positions Kujira favorably in the competitive arena, facilitating ecosystem growth and unlocking new opportunities for collaboration.
- Adaptability: Kujira’s continuous evolution as a blockchain and its dynamic governance process exemplify its adaptability and unwavering commitment to ongoing improvement, laying a solid foundation for navigating the complexities of blockchain technology and adapting to shifting regulatory landscapes.
How is The Kujira Network Secured?
Kujira Network leverages the robust Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus mechanism, a cornerstone of the Cosmos ecosystem. This mechanism implements a Proof of Stake (PoS) approach, where validators are chosen based on their $KUJI token holdings. Staking aligns validators’ interests with the network’s well-being, as misbehavior could result in penalties and the loss of staked tokens.
With a Nakamoto Coefficient of 8, Kujira exhibits a noteworthy level of decentralization. This metric represents the minimum number of validators required to disrupt the blockchain’s operations. Alternatively, it can be viewed as the number of validators or miners holding sufficient mining power or stake to halt or compromise the network.
A higher Nakamoto Coefficient indicates a more decentralized blockchain. However, without a supermajority of two-thirds of validators, new blocks cannot be minted. If consensus on a block cannot be reached, another attempt is made to reassemble the supermajority. Consequently, the network can be temporarily halted, preventing new transactions from being processed.
This inherent characteristic of the Nakamoto Coefficient highlights the delicate balance between decentralization and efficiency in blockchain networks. While a high degree of decentralization enhances security and censorship resistance, it can also pose challenges in achieving rapid consensus and maintaining network responsiveness. Nevertheless, Kujira’s Nakamoto Coefficient of 8 demonstrates its commitment to decentralization while striving to optimize network performance.
Tendermint BFT safeguards the network’s integrity by ensuring that all validators reach a consensus on the ledger’s state, effectively preventing double-spending and other malicious activities. This mechanism functions through a series of rounds, where validators propose blocks, cast votes on these blocks, and finalize the transaction history. This multi-round consensus process safeguards the network’s resilience and reliability, even in the face of node failures or malicious attacks.
The adoption of Tendermint BFT aligns seamlessly with Kujira’s fundamental principles of decentralization, security, and scalability. This mechanism empowers the network to achieve consensus efficiently while upholding a high degree of fault tolerance, rendering it well-positioned to support a flourishing ecosystem of DeFi applications.
Conclusion
Emerging as a meticulously crafted layer 1 blockchain protocol built on the Cosmos SDK, Kujira Network embarks on a mission to democratize access to decentralized finance (DeFi) by providing a comprehensive suite of user-friendly DeFi tools and services.
Kujira Network embodies a governance structure centered around the Kujira Senate, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that enables community members to actively shape the network’s decision-making processes. Through voting and proposal submission, community members exert influence over the network’s trajectory, ensuring it aligns with the collective interests of its stakeholders.
Embedded within Kujira Network’s ethos lies a steadfast commitment to fostering decentralization, ensuring security, and achieving scalability. By harnessing the power of the Cosmos SDK, Kujira seamlessly integrates with other blockchains, expanding its reach within the dynamic DeFi landscape. This cross-chain interoperability unlocks a universe of possibilities for interoperable asset transfers, decentralized applications, and groundbreaking financial solutions.
Overall, Kujira Network epitomizes the transformative potential of DeFi, offering a robust and user-friendly platform that empowers individuals to assume control of their finances and venture into the boundless opportunities of the decentralized ecosystem.
Sources:
https://zerocap.com/insights/research-lab/what-is-kujira-kuji/
https://kujira.app/
https://www.datawallet.com/crypto/bridge-to-kujira
https://docs.kujira.app/dapps-and-infrastructure/blue/ibc-bridge
https://research.tokenmetrics.com/kujira-code-review/
https://medium.com/@cryptocevo/kujira-no-longer-relies-on-some-other-network-e2d14918c4db




