Introduction
Kava, a DeFi platform, merges the best of Ethereum and Cosmos to create a strong and scalable ecosystem for dApps and financial services. Its co-chain setup lets developers create apps using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) or the Cosmos SDK, giving them flexibility and reaching more users.
Project Overview
Kava stands as a Layer-1 blockchain, strategically blending the speed and interoperability of Cosmos with the robust developer capabilities of Ethereum. This fusion is achieved through the utilization of Cosmos EVM technology. Kava is purpose-built to optimize resources for protocol growth, emphasizing scalability, speed, security, and developer support.
Kava operates on a Layer-1 blockchain, utilizing a co-chain architecture that seamlessly integrates the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Cosmos SDK execution environments. This enables developers to build and deploy projects with enhanced scalability and security.
Kava offers DeFi services to crypto users across many blockchain networks, such as stable currencies, bonds, and lending. Kava’s goal is to provide a basis for different open financial services, like security, cross-chain bridges, and modified Chainlink oracles, to enable developers to swiftly design new cross-chain DeFi apps and distribute them to Kava’s worldwide user base.
The lending platform and the built-in cross-chain money market app operate on the Kava blockchain. Together, they form a decentralized bank for digital assets, linking users to products such as stablecoins, loans, and interest-bearing accounts. This setup enables users to enhance their digital assets, do more, and earn more.

Project Background
In the Kava ecosystem, there are three types of tokens: KAVA, USDX stablecoin, and HARD. KAVA is the main token, crucial for the platform’s security, governance, and functions. Users can swap their crypto assets for USDX, Kava’s stablecoin. The HARD token, linked to the HARD Protocol, serves as a governance token, encouraging early participants by giving them a say in the app’s ongoing development and management.
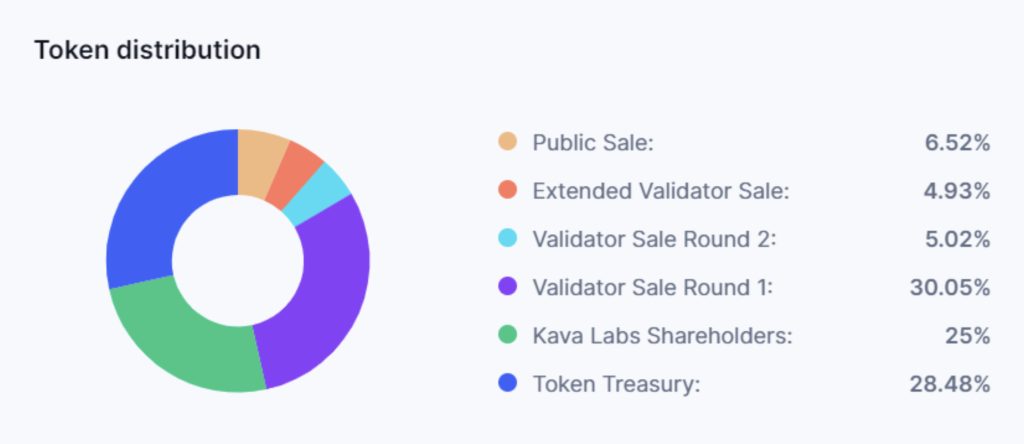
The KAVA token was launched through an ICO that was held from Oct 18th to Oct 24th 2019, and the token allocation was as thus;
Tokenomics
In the Kava ecosystem, there are three types of tokens: KAVA, USDX stablecoin, and HARD. KAVA is the main token, crucial for the platform’s security, governance, and functions. Users can swap their crypto assets for USDX, Kava’s stablecoin. The HARD token, linked to the HARD Protocol, serves as a governance token, encouraging early participants by giving them a say in the app’s ongoing development and management.
The KAVA token was launched through an ICO that was held from Oct 18th to Oct 24th 2019, and the token allocation was as thus;
Use Cases of KAVA Token
KAVA tokens serve multiple purposes within the Kava Network:
Security: The top 100 nodes validate blocks based on a weighted bonded stake in KAVA tokens. Validators are economically incentivized, earning KAVA as block rewards and a portion of the network’s transaction fees. Validators risk losing KAVA through strict slashing conditions, ensuring a commitment to high uptime and transaction integrity.
Governance: It’s used for proposing and voting on important aspects of the Kava Network, like which assets get support, how much debt is allowed, what assets are okay for collateral, collateral ratios, fees, and savings rates for financial tools. People holding KAVA tokens get to cast their votes on proposals that impact the Kava Network’s SAFU (Secure Asset Fund for Users) Fund and where funds are allocated in the treasury.
Incentives: A portion of KAVA emissions serves as incentives for scaling the network. These incentives directly benefit top projects on each chain, fostering growth, competition, and overall ecosystem health.
Core Features and Functionality
Co-chain architecture: Kava offers an Ethereum Co-Chain, an EVM-compatible execution environment designed for Solidity developers and their decentralized applications (dApps). This co-chain not only empowers developers but also ensures scalability and security by leveraging the Kava Network, providing a robust foundation.
Additionally, Kava provides a Cosmos Co-Chain, a highly-scalable and secure blockchain based on the Cosmos SDK. This co-chain serves as a gateway to the extensive Cosmos ecosystem, connecting Kava to 35+ chains and over $60 billion worth of assets through the Inter Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.
Cosmos SDK and Tendermint Core: Built on the Cosmos-SDK, an open-source framework for building Proof-of-Stake blockchains, and leveraging the Tendermint Core consensus engine, Kava ensures Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus for secure and efficient operations.
On-Chain Incentives: Kava introduces a unique approach to developer incentivization through on-chain incentives, with a portion of KAVA emissions directly awarded to protocols. This strategy aims to drive usage and catalyze growth within the Kava ecosystem.
The KavaDAO: The Kava Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), known as KavaDAO, plays a crucial role in governance. Comprising Kava stakers and validators, it operates on a liquid democracy model, allowing active participants to influence decisions related to network functions and incentive distribution.
Advantages of Kava Network
- Seamless Interoperability is a hallmark of Kava’s co-chain architecture, ensuring smooth interactions between Cosmos and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Developers can build in their preferred environment without compromising access to users and assets from both ecosystems.
- The Kava Rise program incentivizes top builders in the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems with on-chain rewards. This approach encourages healthy competition, fosters growth, and enhances the overall health of the Kava ecosystem.
- Optimized Scalability is a key feature, as Kava’s architecture enables the unrestricted flow of users, assets, and projects between Kava and major ecosystems. The lightning-fast Tendermint Core consensus engine further ensures optimized scalability.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability is facilitated by Kava’s unique co-chain architecture, enabling seamless asset transfers and interactions between the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems. This functionality unlocks new opportunities and broadens access for developers and users across different blockchain landscapes.
Risks and Challenges
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are notorious for their volatility, which can impact the value of KAVA tokens. Sudden and significant price fluctuations may affect user confidence and liquidity within the Kava ecosystem.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Despite rigorous audits, smart contracts are not immune to vulnerabilities. Exploitable flaws in the code could lead to security breaches, potentially resulting in financial losses for users and damage to the reputation of the Kava Network.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability Challenges: While Kava’s co-chain architecture aims for seamless interoperability between the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems, technical challenges may arise. Issues related to cross-chain communication, security, or unexpected complexities could pose obstacles to the network’s efficiency.
- Adoption and User Onboarding: Achieving widespread adoption and seamlessly onboarding users into the Kava ecosystem may prove challenging. Educational efforts and user-friendly interfaces are crucial to overcoming barriers and attracting a diverse user base
How The Kava Network Addresses Challenges
- Continuous Security Audits: Kava places a strong emphasis on security. Regular audits by reputable firms, including CertiK, B-Harvest, and Quantstamp, help identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the smart contracts, enhancing the overall security of the platform.
- Active Community Engagement: To mitigate regulatory risks, Kava actively engages with regulatory bodies and complies with evolving legal standards. A transparent and proactive approach to regulatory compliance helps build trust with both users and regulators.
- Robust Governance Model: The KavaDAO, a decentralized autonomous organization, plays a crucial role in addressing challenges. Through decentralized governance, stakeholders actively participate in decision-making processes, fostering a resilient and adaptable network.
- Technical Innovation and Upgrades: Kava’s commitment to technical innovation is evident in its co-chain architecture and ongoing upgrades. By addressing cross-chain interoperability challenges and staying at the forefront of technological advancements, Kava aims to ensure a smooth user experience.
- Community Education and Outreach: To overcome adoption challenges, Kava invests in community education and outreach programs. Providing accessible resources and fostering a supportive community helps newcomers understand and navigate the platform effectively.
Kava Network’s Security
Kava is constructed on the Cosmos framework and utilizes a Tendermint-based proof-of-stake (POS) consensus mechanism to uphold the network’s integrity. This involves a network of validator nodes responsible for validating transactions. Validators, in turn, must deposit collateral to assume this transaction validation duty. In cases of misbehavior or failure to meet stringent requirements, validators face penalties, encouraging them to uphold honesty and efficiency.
Kava token holders can engage in staking nodes to directly earn KAVA rewards from the protocol. However, only the top 100 Kava nodes, also known as validators, qualify for these rewards. Additionally, KAVA holders can stake their tokens on various compatible exchange platforms such as Binance, Kraken, Huobi Pool, and in wallets like Trust Wallet, Cosmostation Wallet, and Keplr.
To ensure the security of Kava’s smart contracts, they undergo audits by multiple independent blockchain and crypto security firms, including CertiK, B-Harvest, and Quantstamp. Importantly, as of now, no vulnerabilities have been discovered in these smart contracts.
Conclusion
Kava operates as a Layer-1 blockchain, leveraging the best features of both Cosmos and Ethereum to deliver decentralized financial services. Through its co-chain structure, on-chain incentives, and decentralized governance, Kava strives to furnish a flexible platform catering to developers and users spanning diverse blockchain ecosystems. Kava Network stands out as a noteworthy DeFi initiative. Its co-chain design, inventive incentive systems, and solid governance structure position it as a compelling candidate for future expansion and widespread adoption.




