What is Layer Zero and How it Works
Layer zero blockchain is the first stage of blockchain that enables the operation of various networks such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others.
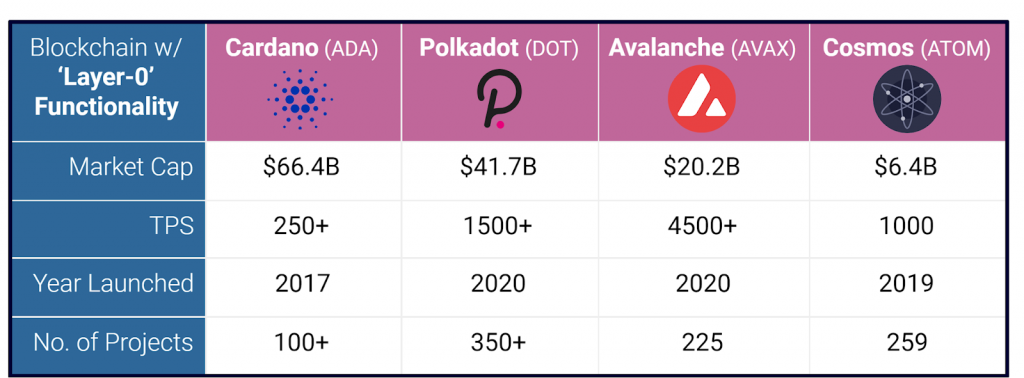
Layer 0 blockchain protocols such as Cosmos and Polkadot create an entire ecosystem of networks with exceptional cross-chain interoperability by utilizing a decentralized network of independent parallel blockchains.
Layer 0 protocols are made up of a series of state channels that use user-defined functions to validate data. This layer, in addition to the hardware, servers, and systems, includes nodes and any device connected to the nodes. It supports several consensus algorithms and P2P systems to optimize network topology, including proof of work, proof of stake, proof of activity, proof of reputable observations, directed acyclic graphs DAG, and others.
Layer 0 adds to the three major pillars of blockchain scalability, neutrality, and adaptability by supporting block encryption and concealing the origin of the block via peer-to-peer relaying. Native tokens serve as the core consensus layer, offering economic incentives to users to contribute to and sustain the ecosystem within the HGTP network, resulting in a win-win situation in which all participants are equally rewarded for their efforts. You must stake or purchase the platform’s native token in order to build a business using the Layer 0 protocol. By acquiring the relevant tokens within the blockchain network, you will gain complete access to the Layer 0 ecosystem, data-rich solutions, innovative solutions, and products. Once you’ve obtained the required tokens, you can use them to create unique tokens, business tokens, and so on.

Layer Zero Team
Co-founded by Bryan Pellegrino, Ryan Zarick, and Caleb Banister.
LayerZero is developed by LayerZero Labs, a Vancouver-based startup that develops protocols to enable omnichain decentralized applications across multiple blockchains. The company was co-founded in 2021 by Bryan Pellegrino, Ryan Zarick, and Caleb Banister, who have worked together in computer network research labs at the University of New Hampshire.
Problems Layer Zero Solve
- Interoperability: It refers to the ability of blockchain networks to communicate with one another. This property enables a more tightly interwoven network of blockchain-enabled products and services, which in turn offers a better user experience. Blockchain networks built on the same Layer 0 protocol can interact with one another by default, without the need for dedicated bridges. Using different iterations of cross-chain transfer protocols, Layer 0 allows an ecosystem’s blockchains to build upon one another’s features and use cases. Some common outcomes of this are enhanced transaction speeds and greater efficiency.
- Scalability: A monolithic blockchain such as Ethereum is often congested because a single Layer 1 protocol is providing all the critical functions, such as transaction execution, consensus, and data availability. This creates a bottleneck for scaling that Layer 0 can alleviate by delegating these critical functions to different blockchains. This design ensures that blockchain networks built upon the same Layer 0 infrastructure can each optimize certain tasks, thereby enhancing scalability. For example, execution chains can be optimized to handle high numbers of transactions per second.
- Developer flexibility: To encourage developers to build on them, Layer 0 protocols often provide easy-to-use software development kits, SDKs, and a seamless interface to ensure developers can easily launch their purpose-specific blockchains. Layer 0 protocols give developers great flexibility to customize their blockchains, allowing them to define their token issuance models and control the type of DApps they want to be built on their blockchains.
Use Cases of Layer Zero
The Layer 0 protocol can be used across several use cases, including data validation, setting up individual reward structures, digital currency wrapping, and more. It serves as the root layer, allowing cross-chain interoperability with all Layer 1 protocols like BTC, ADA, and ETH.
Sources:
https://zebpay.com/blog/what-is-blockchain-layer-0-1-2-and-3
(https://boxmining.com/layerzero-token/#Who_is_the_Team_behind_LayerZero
https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/glossary/layer-0




