Introduction
Chainlink is a project that aims to create a decentralized oracle network for smart contracts. Chainlink is a middleware that connects blockchain-based smart contracts with external data, such as market prices, weather data, sports scores, and more. Chainlink enables smart contracts to access real-world data and events, and execute accordingly, without relying on centralized or trusted intermediaries. In this article, we will explore the project overview, background, tokenomics, features and functionality, roadmap and future developments, risks and challenges, and conclusion of Chainlink.
Overview
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that bridges the gap between blockchains and the real world. An oracle is a service that provides data or computation to smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements that run on blockchains. However, most blockchains are isolated and cannot access external data or systems, due to their security and consensus mechanisms. This limits the scope and functionality of smart contracts, and makes them dependent on centralized oracles, which are prone to manipulation, corruption, or failure.
Chainlink solves this problem by providing a decentralized and trustless way for smart contracts to interact with any external data source or system, such as web APIs, data feeds, cloud services, IoT devices, payment systems, and more. Chainlink leverages a network of independent node operators, who provide and verify data or computation to smart contracts, and receive rewards in the form of LINK tokens, the native cryptocurrency of Chainlink. Chainlink also employs various mechanisms to ensure the quality, reliability, and security of the data or computation, such as reputation systems, aggregation methods, cryptographic proofs, and economic incentives.
Chainlink is blockchain-agnostic, meaning that it can connect any smart contract platform to any external data source or system, regardless of the underlying blockchain protocol or architecture. Chainlink supports various smart contract platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Solana, and more. Chainlink also supports various external data sources and systems, such as market data providers, weather data providers, sports data providers, and more.
Background

Chainlink was founded in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, who co-authored a white paper introducing the Chainlink protocol and network with Cornell University professor Ari Juels the same year. Nazarov and Ellis are also the co-founders of SmartContract, a company that provides oracle solutions for smart contracts since 2014. Nazarov and Ellis have extensive experience and expertise in the blockchain and smart contract fields, and are passionate about creating a more connected and decentralized world.
Chainlink was launched to the public in 2019, after two years of research and development. Chainlink is named after the concept of linking smart contracts to external data sources or systems, which are often referred to as “off-chain” or “outside the chain”. LINK, the native cryptocurrency of Chainlink, is named after the network of node operators who provide and verify data or computation to smart contracts, and are often referred to as “linkers” or “chainlinkers”. Since its launch, Chainlink has achieved several milestones, such as:
– Securing over $75 billion in value for leading DeFi protocols, such as Aave, Synthetix, Compound, and more2
– Providing data or computation for various sectors and industries, such as gaming, insurance, identity, supply chain, and more3
– Integrating with various smart contract platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Solana, and more4
– Partnering with various enterprises and organizations, such as Google, Oracle, SWIFT, UNICEF, and more.
– Launching various products and services, such as Chainlink VRF, Chainlink Keepers, Chainlink OCR, and more.
Tokenomics
LINK is the native utility token of Chainlink, and it is used for the following functions:
Payment: Users can use LINK to pay for the data or computation services provided by the node operators on the Chainlink network. Node operators can set their own prices for their services, and receive LINK as compensation for their work.
Incentive: Users can use LINK to incentivize the node operators to provide and verify high-quality, reliable, and secure data or computation to smart contracts. Node operators can stake LINK as collateral for their services, and lose LINK as a penalty for providing inaccurate or malicious data or computation.
Governance: Users can use LINK to participate in the governance and development of the Chainlink network, by voting on proposals and changes to the protocol, and influencing the direction and vision of the project.
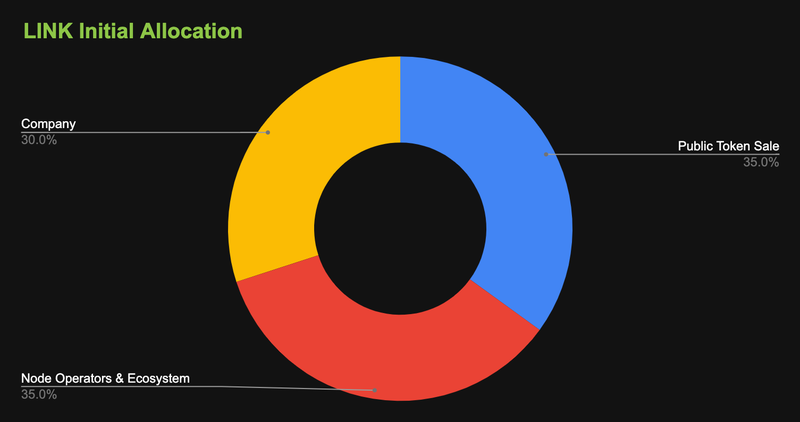
The total supply of LINK is 1,000,000,000 and the current circulating supply is 453,509,553 (~45.35% of the total token supply) as of November 12, 2023. The token distribution of LINK is as follows:
Node Operators: 35% (350,000,000 LINK), allocated for the node operators who provide and verify data or computation to smart contracts, and receive LINK as rewards and incentives.
Team: 30% (300,000,000 LINK), allocated for the team members who develop and maintain the Chainlink network, and receive LINK as compensation and vesting.
Token Sale: 35% (350,000,000 LINK), sold to the public and private investors who supported the project in 2017 and 2019, at an average price of $0.11 per LINK.
Users can buy, store, and trade LINK on various platforms, such as:
Chainlink: Users can use the official Chainlink platform and website to access various features and functionalities of the network, such as the Chainlink Market, the Chainlink Docs, and the Chainlink Blog.
Binance: Users can trade LINK with other tokens on Binance, a centralized exchange that supports Chainlink and other blockchain projects.
Coinbase: Users can trade LINK with other tokens on Coinbase, a centralized exchange that supports Chainlink and other blockchain projects.
Uniswap: Users can swap LINK with other tokens on Uniswap, a decentralized exchange that supports Chainlink and other Ethereum-based projects.
MetaMask: Users can store and manage LINK and other Ethereum-based tokens on MetaMask, a browser extension wallet that supports Chainlink and other Ethereum-based projects.
Ledger: Users can store and manage LINK and other Ethereum-based tokens on Ledger, a hardware wallet that supports Chainlink and other Ethereum-based projects.

Features and Functionality
Chainlink offers a suite of features and functionality that power the smart contract revolution, such as:
Data Feeds: Users can access various data feeds on the Chainlink network, such as market prices, weather data, sports scores, and more. These data feeds are provided and verified by multiple node operators, and aggregated and delivered to smart contracts, ensuring high-quality, reliable, and secure data. These data feeds can be used to power various smart contract applications, such as DeFi, gaming, insurance, and more.
VRF: Users can access a verifiable random function (VRF) on the Chainlink network, which is a cryptographic method that generates a random number that can be verified on-chain. This VRF can be used to ensure fair and transparent outcomes in various smart contract applications, such as gaming, NFTs, and more.
Keepers: Users can access a decentralized automation service on the Chainlink network, which is a network of node operators that monitor and execute smart contract functions based on predefined conditions, such as time or events. This service can be used to automate various smart contract tasks, such as rebalancing, liquidation, harvesting, and more.
OCR: Users can access an off-chain reporting (OCR) protocol on the Chainlink network, which is a scalability solution that reduces the on-chain gas costs and latency of data delivery, by aggregating and compressing data off-chain, and broadcasting it on-chain using a single transaction. This protocol can be used to increase the efficiency and performance of data feeds and other oracle services.
CCIP: Users can access a cross-chain interoperability protocol (CCIP) on the Chainlink network, which is a cross-chain communication protocol that enables the exchange of data and value between different blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, Polkadot, and more. This protocol can be used to enable cross-chain smart contract applications, such as cross-chain swaps, loans, and more.
Some of the unique selling points and advantages of Chainlink are:
Decentralization and Trustlessness: Chainlink is a decentralized and trustless network, where no single entity or authority controls or influences the data or computation services provided by the node operators. Chainlink also employs various mechanisms to ensure the quality, reliability, and security of the data or computation, such as reputation systems, aggregation methods, cryptographic proofs, and economic incentives.
Blockchain-Agnostic and Universal: Chainlink is a blockchain-agnostic and universal network, where it can connect any smart contract platform to any external data source or system, regardless of the underlying blockchain protocol or architecture. Chainlink supports various smart contract platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Solana, and more. Chainlink also supports various external data sources and systems, such as market data providers, weather data providers, sports data providers, and more.
Developer-Friendly and Flexible: Chainlink is a developer-friendly and flexible network, where it provides various resources and tools for developers to easily and quickly integrate Chainlink services into their smart contract applications, such as the Chainlink Docs, the Chainlink Market, the Chainlink Testnet, and more. Chainlink also allows developers to customize and optimize their oracle services according to their needs and preferences, such as the such as the data source, the frequency, the security, and the cost.
Roadmap and Future Development
Chainlink has an ambitious roadmap and vision for the future development of the project and the ecosystem. Some of the goals and objectives of Chainlink are:
– Expanding the network of node operators and data providers, and increasing the diversity and quality of the data and computation services available on the Chainlink network.
– Enhancing the scalability and performance of the Chainlink network, by implementing various solutions, such as OCR, CCIP, and layer-2 integrations, which reduce the on-chain gas costs and latency of data delivery, and increase the throughput and capacity of the network.
– Extending the functionality and utility of the Chainlink network, by launching various products and services, such as VRF, Keepers, DECO, and Town Crier, which enable new and innovative use cases for smart contracts, such as gaming, NFTs, identity, privacy, and more.
– Collaborating with various smart contract platforms and blockchain networks, and supporting the interoperability and collaboration of various protocols and platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Solana, and more.
– Partnering with various enterprises and organizations, and supporting the adoption and integration of Chainlink services into various sectors and industries, such as finance, insurance, supply chain, gaming, and more.
Risks and Challenges
Chainlink faces some potential risks and challenges that may affect the project and the ecosystem, such as:
Competition: Chainlink competes with other oracle networks and services, such as Band Protocol, API3, The Graph, and more. Chainlink needs to maintain its competitive edge and differentiation by offering superior decentralization, trustlessness, blockchain-agnosticism, developer-friendliness, and flexibility, and attracting more users and developers to its network.
Adoption: Chainlink needs to increase its adoption and usage, by creating more value and utility for its users and developers, and supporting more use cases and applications that can benefit from its network. Chainlink also needs to overcome the network effects and switching costs that may hinder its adoption and growth.
Regulation: Chainlink operates in a highly uncertain and evolving regulatory environment, where different jurisdictions may have different rules and requirements for oracle and smart contract services. Chainlink needs to comply with the relevant laws and regulations, and avoid any legal or regulatory issues that may affect its operations and reputation.
Chainlink addresses these challenges by:
Innovation: Chainlink strives to innovate and improve its features and functionality, and offer the best user experience and value proposition for its users and developers. Chainlink also leverages the innovation and collaboration of its team and partners, who have extensive experience and expertise in the oracle and smart contract fields, and integrates with the latest technologies and developments in the industry.
Education: Chainlink strives to educate and inform its users and developers, by providing various resources and tools, such as the Chainlink Docs, the Chainlink Blog, the Chainlink Academy, and more. Chainlink also strives to educate and inform the public and the regulators, by providing various reports and publications, such as the Chainlink Whitepaper, the Chainlink Research, the Chainlink Podcast, and more.
Community: Chainlink strives to build and nurture its community, by providing various platforms and channels, such as the Chainlink Forum, the Chainlink Reddit, the Chainlink Telegram, and more. Chainlink also strives to engage and empower its community, by providing various opportunities and incentives, such as the Chainlink Hackathons, the Chainlink Grants, the Chainlink Nodes, and more.
Conclusion
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that bridges the gap between blockchains and the real world. Chainlink is a middleware that connects blockchain-based smart contracts with external data, such as market prices, weather data, sports scores, and more. Chainlink enables smart contracts to access real-world data and events, and execute accordingly, without relying on centralized or trusted intermediaries. Chainlink leverages a network of independent node operators, who provide and verify data or computation to smart contracts, and receive rewards in the form of LINK tokens, the native cryptocurrency of Chainlink. Chainlink also employs various mechanisms to ensure the quality, reliability, and security of the data or computation, such as reputation systems, aggregation methods, cryptographic proofs, and economic incentives. Chainlink is a project that is worth following and supporting, as it contributes to the smart contract revolution and the blockchain industry.
Sources:
https://chain.link/
https://docs.chain.link/
https://blog.chain.link/
https://market.link/
https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/chainlink/




