Introduction to Radix
Radix is a forward-thinking cryptocurrency project with the ambition to create a decentralized and scalable platform for building and deploying decentralized applications (DApps). At its core, Radix is on a mission to tackle the scalability issues that have hindered many existing blockchain networks. In this comprehensive article, we’ll take a thorough dive into the world of Radix, delving into its origins, technological foundations, tokenomics, security measures, practical use cases, and beyond.
Project Overview of Radix
Radix is an ambitious cryptocurrency project with a primary objective, to establish a decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem that can effectively scale and handle the growing demands of the blockchain world. At its core, Radix seeks to overcome one of the most significant challenges facing blockchain networks today – scalability.
To achieve this, Radix has developed a unique consensus mechanism and architecture that set it apart from many other blockchain platforms. Cerberus combines a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus algorithm with a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure to address scalability challenges. The BFT consensus ensures robust security and consensus among all network nodes, while the DAG structure allows for parallel processing of transactions, significantly improving throughput and scalability. Additionally, Radix employs sharding, dividing the network into smaller shards that operate independently, further enhancing scalability. Data compression techniques are also utilized to optimize transaction data storage and processing efficiency. Together, Cerberus offers a promising solution to scalability issues, making Radix a standout project in the blockchain ecosystem.
The project aims to not only provide a scalable infrastructure but also make it accessible for developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) that can revolutionize various industries. By addressing scalability issues and offering a user-friendly development environment, Radix hopes to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology for real-world applications.

The Background of Radix
Dan Hughes, hailing from the UK, embarked on his journey with Bitcoin back in 2012, driven by his background in telecommunications technology. Recognizing the transformative potential of blockchain technology, particularly in the realm of global finance, he dived into extensive Bitcoin research for a year. It was in May 2013 that he initiated the eMunie project, which later transformed into Radix, introducing it on Bitcointalk.
For the subsequent five years, Dan Hughes diligently tackled one of the most pressing challenges of the blockchain world: scalability. He embarked on a journey of innovation, conceptualizing and testing various consensus architectures. These included Blocktrees, Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), Channelled Asynchronous State Trees (CAST), Tempo, and Cerberus.
In 2017, Piers Ridyard assumed the role of CEO, and with this shift, the project underwent a transformation, rebranding as Radix. The endeavor also secured crucial funding from notable figures like Taavet Hinrikus, co-founder of TransferWise, and LocalGlobe, a prominent European venture capital firm.
The year 2020 marked a turning point with the emergence of Cerberus, which introduced the world to the first cross-shard atomically composable consensus protocol, promising limitless linear scalability. Concurrently, Radix Tokens (Jersey) Limited, the entity based in Jersey (Channels Islands), issued XRD and assumed responsibility for safeguarding the Radix Foundation’s treasury, led by CEO Andrew Jarrett.
Fast-forward to July 2021, and the Radix Public Network’s maiden iteration, known as “Olympia,” became operational. This significant milestone paved the way for the release of Scrypto, a groundbreaking DeFi development language, in December 2021.
Looking ahead, Radix’s “Babylon” release is slated for the first half of 2023, promising the integration of production smart contracts written in Scrypto onto the mainnet, signaling the project’s continued evolution and innovation.
Tokenomics
The native token of Radix is XRD. XRD can be purchased on Bitfinex, Bitmart, Digifinex, Gate.io, LBank, MEXC.
Radix employs a deflationary token model with a fixed initial supply. The total supply of Radix tokens, known as XRD, is capped at 21 billion XRD. Unlike some projects that rely on mining or staking mechanisms for token distribution, Radix initially allocated tokens through private sales, partnerships, and a public sale.
A significant portion of the token supply was set aside for the Radix Reserve, accounting for approximately 50% of the total supply. These tokens are designed to be used for the ongoing development and maintenance of the Radix platform, ensuring its sustainability and growth.
One intriguing aspect of Radix’s tokenomics is its deflationary design. The platform employs mechanisms to reduce the token supply over time. A portion of transaction fees, for instance, is burned, permanently removing XRD tokens from circulation. This deflationary approach can create scarcity and potentially contribute to the token’s long-term value appreciation.
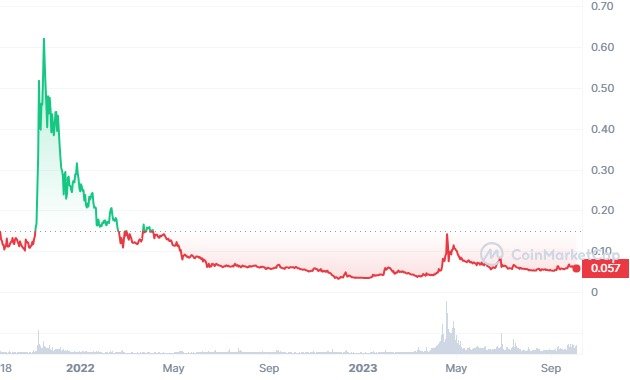
Market Cap: $590,722,732
Circulating Supply: 10,258,653,992 XRD
Supply Cap: 12,658,779,442 XRD
All time high: $0.6538 (-91.25%) 14th November, 2021
All time low: $0.03154 (+81.35%) 30th November, 2022
Role of XRD in the Radix Ecosystem
XRD serves as the native utility token within the Radix ecosystem, playing several crucial roles:
-
Transaction Fees: XRD is used to pay for transaction fees on the Radix network, similar to how gas fees function on the Ethereum network. This ensures that users have a financial stake in the network’s security and operation.
-
Staking: Radix implements a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, allowing XRD holders to participate in network security and consensus by staking their tokens. In return, stakers may earn rewards in the form of additional XRD tokens.
-
Governance: XRD holders have governance rights, enabling them to participate in protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, and decision-making processes through a decentralized governance system. This empowers the community to steer the future development of Radix.
-
Incentives: To foster network growth and adoption, Radix may distribute XRD tokens as incentives to developers, validators, and participants in various ecosystem activities, encouraging active engagement within the Radix network.

Features and Functionality of Radix
Radix stands out as a project with a unique vision and a set of core features designed to address some of the most pressing challenges facing the industry. Some of which include:
Linear Scalability: Scalability has been a persistent concern in the blockchain world, often leading to issues like slow transaction speeds and high fees. Radix tackles this problem head-on by offering linear scalability. Unlike some blockchain networks that slow down as they grow, Radix’s architecture ensures that its performance improves as more participants join the network. This linear scalability is achieved through the innovative Cerberus consensus protocol, which allows Radix to process an ever-increasing number of transactions efficiently.
Cross-Shard Compatibility: Sharding is a common approach to scalability, but it can sometimes lead to fragmentation and limited interoperability between different shards. Radix, however, has devised a solution to this problem. The network’s unique consensus mechanism enables cross-shard compatibility, allowing assets and data to flow seamlessly between different parts of the network. This opens the door to a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) and use cases that can benefit from a high degree of interaction.
Scrypto: A User-Friendly Development Language: Building on Radix is made accessible to developers with the introduction of Scrypto. This innovative development language simplifies the process of creating smart contracts and decentralized applications. Scrypto’s user-friendly nature lowers the barrier to entry for developers, fostering innovation and expanding the Radix ecosystem.
Deflationary Tokenomics: The XRD token, Radix’s native cryptocurrency, plays a pivotal role in the network. Radix employs a deflationary tokenomics model, where a portion of transaction fees is burned, reducing the token supply over time. This deflationary mechanism can potentially create scarcity, increasing the value of XRD tokens while ensuring that participants have a financial stake in the network’s security and operation.
Decentralized Governance: Radix places governance in the hands of the community through decentralized governance mechanisms. XRD token holders have the power to participate in protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, and key decision-making processes. This democratic approach ensures that the Radix network evolves in a way that aligns with the interests and values of its user base.
Use Cases of Radix
Radix, with its unique features and innovative design, offers a versatile platform with a multitude of compelling use cases. Let’s explore some of the practical applications that Radix brings to the table.
DeFi Ecosystem: Radix’s scalability and cross-shard compatibility make it an ideal platform for hosting DeFi applications. Developers can leverage Radix to create decentralized exchanges, lending protocols, and yield farming platforms that can handle high transaction volumes efficiently.
NFT Marketplaces: Radix’s ability to process a large number of transactions in parallel makes it suitable for NFT marketplaces. Artists and creators can utilize Radix to mint, trade, and showcase their NFTs securely and at a lower cost.
Gaming Industry: Radix’s linear scalability and user-friendly development language, Scrypto, are assets for creating blockchain-based games. Gaming studios can leverage Radix to build immersive and secure gaming experiences with unique tokenized assets.
Tokenization of Assets: Tokenization involves converting real-world assets like real estate, art, or commodities into digital tokens. Radix’s deflationary tokenomics and cross-shard compatibility enable the efficient creation and management of tokenized assets.
Cross-Border Payments: Its efficient consensus mechanism and low transaction costs can significantly reduce the time and fees associated with international money transfers.
Advantages, Risks and Challenges
Advantages of Radix:
-
Scalability: Radix shines in the scalability department. Unlike some blockchain platforms that grapple with slow transaction speeds and congestion, Radix’s architecture is built to handle high transaction volumes efficiently. This scalability opens doors to applications that demand fast and seamless interactions.
-
Cross-Shard Compatibility: Radix’s cross-shard compatibility is a game-changer. It allows developers to create decentralized applications that can span multiple shards, fostering interoperability and expanding the possibilities for building complex ecosystems.
-
User-Friendly Development: Radix introduces Scrypto, a development language designed to simplify the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications. Its user-friendly nature empowers developers to bring their ideas to life without the steep learning curve associated with some other blockchain languages.
-
Deflationary Tokenomics: The tokenomics of Radix feature a deflationary mechanism that can potentially encourage long-term holding and reduce inflationary pressures. This can be an attractive feature for investors and users of the network.
-
Secure and Decentralized: Radix prioritizes security and decentralization, which are fundamental tenets of blockchain technology. Its consensus mechanisms and governance model aim to ensure the network’s integrity and resist centralization.
Risks and Challenges:
-
Competition: The blockchain space is fiercely competitive, with numerous projects vying for attention and adoption. Radix faces the challenge of standing out in a crowded field and convincing developers and users to choose its platform.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: Like all blockchain projects, Radix operates in a regulatory landscape that is still evolving. Navigating potential regulatory changes and compliance requirements can be challenging and could impact the project’s future.
-
Adoption Hurdles: Achieving widespread adoption is a hurdle for many blockchain platforms. Radix must attract developers and businesses to build on its network, and users must see value in adopting Radix-powered applications.
-
Security Concerns: As a blockchain platform, Radix must remain vigilant against potential security threats, such as smart contract vulnerabilities and network attacks. Robust security measures are essential to maintain user trust.
-
Technical Complexity: While Radix aims to simplify development with Scrypto, building decentralized applications can still be technically complex. Developers may face a learning curve when working with new blockchain technologies.
Conclusion
Radix’s journey in the blockchain space is marked by promise and ambition. Its strengths in scalability, cross-shard compatibility, user-friendly development, and tokenomics make it a formidable contender. However, the challenges of competition, regulatory dynamics, adoption, security, and technical complexity loom large. As Radix continues to evolve, it will need to navigate these waters while demonstrating the real-world value it brings to the blockchain ecosystem. Time will tell how this innovative project fares in the ever-changing landscape of decentralized technologies.
Sources
https://www.radixdlt.com/
https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/radix-protocol/
https://learn.radixdlt.com/article/start-here-radix-tokens-and-tokenomics




